In the landscape of healthcare, two prominent paradigms often emerge in discussions: pharmacy and holistic medicine. Each offers unique perspectives, benefits, and challenges, creating a complex tapestry of choices for patients seeking wellness. This article delves into both approaches, examining their philosophies, practices, and implications for health, while also considering which might be best suited for individuals.
The Foundations of Pharmacy
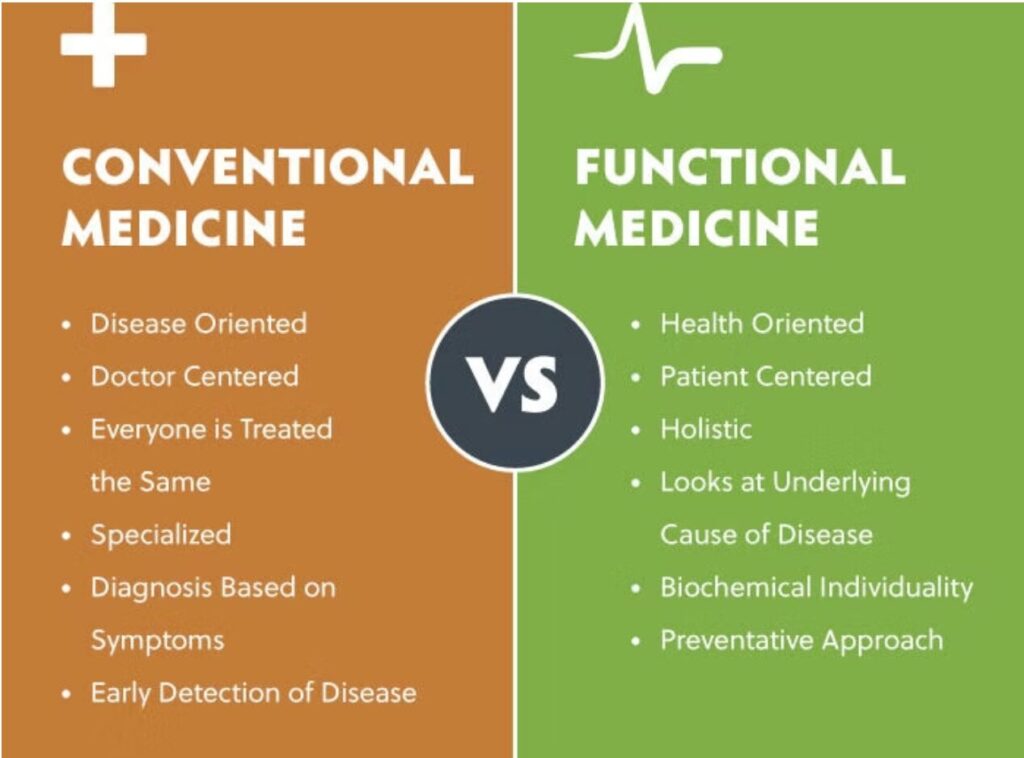
Pharmacy is rooted in a scientific approach to health care, focusing on the preparation, dispensation, and appropriate use of medications. Pharmacists, armed with extensive training in pharmacology, biochemistry, and therapeutic knowledge, serve as critical intermediaries between patients and medications. Their expertise enables them to guide patients on proper medication usage, potential side effects, and drug interactions.
Benefits of Pharmacy
1. Evidenced-Based Practice: One of the primary advantages of pharmacy is its reliance on rigorous scientific research. Medications are subjected to extensive clinical trials to ascertain their safety and efficacy, offering a reliable foundation for treatment.
2. Immediate Relief: For acute conditions, pharmaceutical interventions can provide quick relief. Antibiotics for infections or analgesics for pain demonstrate how medications can effectively address urgent health issues.
3. Chronic Disease Management: Pharmacists play a vital role in managing chronic diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, and asthma. Through medication therapy management, pharmacists help patients achieve optimal therapeutic outcomes.
4. Accessibility and Expertise: With a growing number of pharmacists practicing in various settings—from retail chains to hospitals—the accessibility of pharmaceutical care is increasing. Pharmacists often provide valuable consultation services, answering patient questions and educating them about their medications.
Challenges of Pharmacy
1. Side Effects and Adverse Reactions: While medications can be life-saving, they are not without risks. Side effects range from mild to severe, and adverse drug reactions can lead to hospitalizations.
2. Over-Reliance on Medications: There is a concern that the healthcare system often defaults to pharmacological solutions rather than exploring lifestyle modifications or alternative therapies.
3. Cost: Prescription medications can be expensive, especially for those without adequate insurance coverage. This financial burden can limit access to necessary treatments.
4. Fragmentation of Care: Patients may receive prescriptions from multiple providers without sufficient coordination, leading to potential medication errors and reduced efficacy of treatments.
The Principles of Holistic Medicine
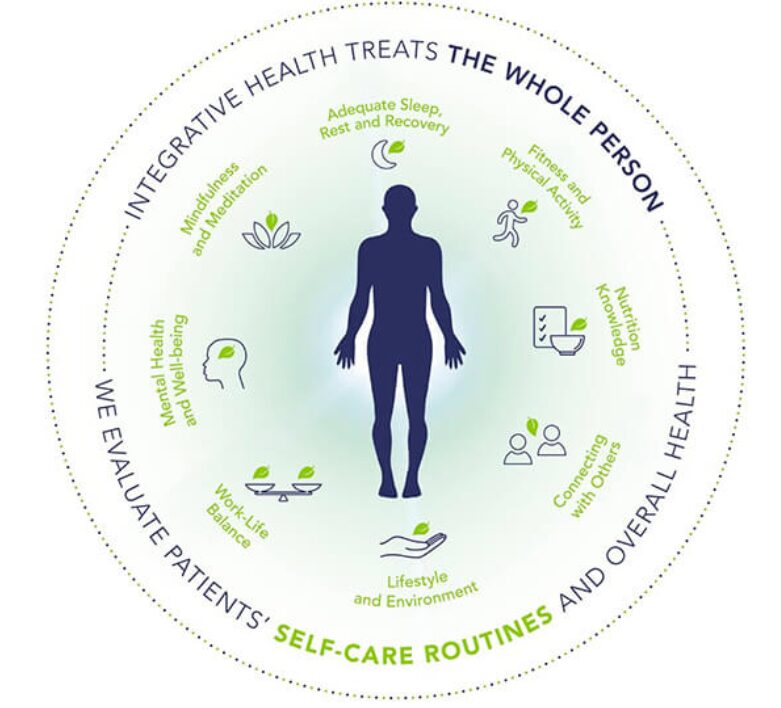
Holistic medicine embodies a philosophy that emphasizes treating the whole person—body, mind, and spirit—rather than just the symptoms of disease. This approach integrates conventional medical practices with complementary therapies, such as acupuncture, herbal medicine, and nutritional counseling. Practitioners of holistic medicine often seek to understand the underlying causes of illness and aim for overall wellness.
Benefits of Holistic Medicine
1. Personalized Care: Holistic practitioners typically spend more time with patients, allowing for a comprehensive assessment of their physical, emotional, and spiritual well-being. This can foster a deeper doctor-patient relationship and tailor treatments to individual needs.
2. Focus on Prevention: Holistic medicine often emphasizes preventive care through lifestyle changes, including diet, exercise, and stress management. This proactive approach can reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
3. Natural Therapies: Many holistic practices utilize natural remedies and therapies, which may have fewer side effects than conventional medications. This aspect appeals to patients seeking alternatives to pharmaceuticals.
4. Integration of Mind-Body Connection: Holistic medicine recognizes the impact of mental and emotional health on physical well-being, addressing stress, anxiety, and other psychological factors that can contribute to illness.
Challenges of Holistic Medicine
1. Lack of Scientific Evidence: While many holistic practices have anecdotal support, the scientific evidence backing their efficacy is often limited. This can lead to skepticism from the broader medical community.
2. Regulatory Issues: The regulation of holistic practitioners varies widely, leading to concerns about qualifications and standards of care. Patients may struggle to identify qualified practitioners.
3. Delayed Treatment: In some cases, reliance on holistic methods may delay access to effective conventional treatments, potentially worsening a patient’s condition.
4. Insurance Coverage: Many holistic therapies are not covered by insurance, creating financial barriers for patients seeking alternative treatments.
A Comparative Analysis
When considering pharmacy and holistic medicine, it’s essential to evaluate how each perspective addresses the complexities of health and disease.
Treatment Philosophy
– Pharmacy emphasizes a symptom-based approach, often focusing on alleviating specific health issues through medication.
– Holistic medicine seeks to understand and address the root causes of illness, advocating for comprehensive lifestyle changes alongside treatment.
Patient Experience
– Pharmacy provides quick solutions but may lack the depth of engagement found in holistic practices.
– Holistic medicine fosters deeper relationships and a sense of empowerment but can be time-consuming and potentially less immediately effective.
Cost and Accessibility
– Pharmaceuticals can be costly, but they are often more readily available and covered by insurance.
– Holistic therapies may offer more affordable natural options, but lack of insurance coverage can make them less accessible for many.
Finding the Right Balance
The question of which approach is best ultimately depends on individual circumstances, preferences, and health needs. Some patients may thrive on the immediate relief offered by pharmaceuticals, while others may prefer the personalized care of holistic methods.
Personalizing Your Healthcare Journey
1. Assessing Individual Needs: Patients should consider their health conditions, treatment goals, and personal values. For example, someone managing chronic pain may benefit from a combination of medications and holistic practices such as acupuncture or mindfulness.
2. Collaboration Between Approaches: Integrative medicine, which combines conventional and alternative therapies, is gaining traction. Patients can seek practitioners who embrace this model, allowing for a more comprehensive approach to health.
3. Open Communication: Engaging in open dialogues with healthcare providers about treatment options fosters a collaborative environment. Patients should feel empowered to ask questions and express concerns about their care.
4. Educating Oneself: Knowledge is a powerful tool. Patients can research both pharmacy and holistic options, considering evidence-based practices alongside personal experiences.
Conclusion
In the ongoing debate between pharmacy and holistic medicine, there is no one-size-fits-all answer. Each approach presents its own set of benefits and challenges, influencing how individuals navigate their health journeys. By understanding the strengths and limitations of both paradigms, patients can make informed choices that align with their values and health needs.
As healthcare continues to evolve, a more integrative approach that respects both the scientific rigor of pharmacy and the compassionate understanding of holistic medicine may emerge. Ultimately, the best path is one that prioritizes the patient, fostering a health care environment that embraces diverse perspectives and holistic well-being.
In this multifaceted world of healthcare, the journey to wellness is as unique as the individuals seeking it.