Artificial Intelligence (AI) is undeniably at the forefront of technological advancements in the 21st century, poised to reshape industries, economies, and the nature of work itself. The impact of AI on employment is a topic of significant debate and concern, with proponents and skeptics offering divergent perspectives on its potential consequences.

Understanding Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are programmed to think and learn like humans. This field encompasses a broad range of technologies, from machine learning algorithms that can recognize patterns and make predictions, to natural language processing systems capable of understanding and generating human language, to robotics that can perform physical tasks autonomously.
The rapid development of AI has been driven by advancements in computing power, the availability of vast amounts of data, and breakthroughs in algorithms. These factors have collectively enabled AI systems to achieve levels of performance previously thought impossible, leading to their widespread adoption across various sectors such as healthcare, finance, transportation, and entertainment.
The Promise of AI
Proponents of AI argue that its adoption will lead to numerous benefits for society. These include increased productivity and efficiency, improved decision-making processes, enhanced personalization of services, and the ability to tackle complex challenges such as climate change and disease prevention. AI-powered technologies have already demonstrated their potential to revolutionize industries by automating repetitive tasks, optimizing workflows, and enabling innovations that were once confined to the realm of science fiction.
In healthcare, for instance, AI-driven diagnostic tools can analyze medical images with greater accuracy than human experts, leading to earlier detection of diseases and improved patient outcomes. Similarly, in agriculture, AI-powered systems can optimize crop yields by analyzing data on soil quality, weather patterns, and crop health, thereby ensuring food security in an increasingly volatile climate.
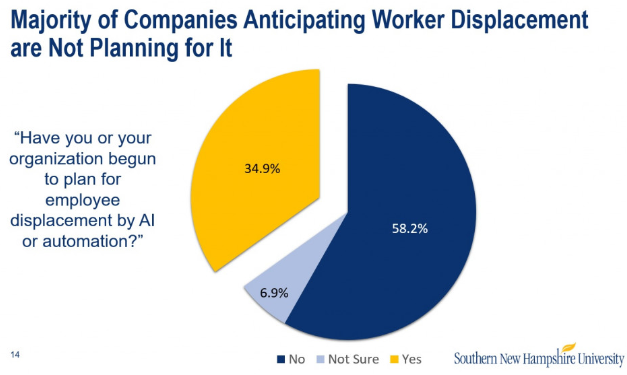
The Challenge of Displacement
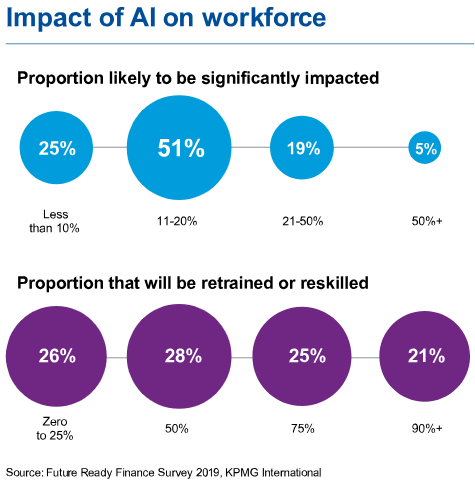
However, the widespread adoption of AI also raises concerns about its impact on employment. Critics argue that AI technologies have the potential to automate a significant number of jobs, leading to widespread displacement of workers across various sectors. Jobs that involve routine, predictable tasks are particularly susceptible to automation, including roles in manufacturing, transportation, customer service, and administrative support.
For example, autonomous vehicles powered by AI threaten to disrupt the transportation industry by eliminating the need for human drivers. Similarly, advancements in natural language processing have enabled chatbots and virtual assistants to handle customer inquiries and support requests without human intervention, potentially reducing the demand for customer service representatives.
The Transformation of Work
While AI may lead to the displacement of certain jobs, proponents argue that it will also create new opportunities and transform the nature of work itself. AI technologies have the potential to augment human capabilities, enabling workers to focus on tasks that require creativity, critical thinking, and emotional intelligence—skills that are difficult to replicate with current AI capabilities.
In healthcare, for instance, AI-powered tools can assist medical professionals by automating routine tasks such as administrative paperwork and data entry, allowing doctors and nurses to spend more time interacting with patients and delivering personalized care. Similarly, in education, AI-driven platforms can personalize learning experiences for students based on their individual strengths and weaknesses, thereby improving educational outcomes and preparing students for the demands of the 21st-century workforce.
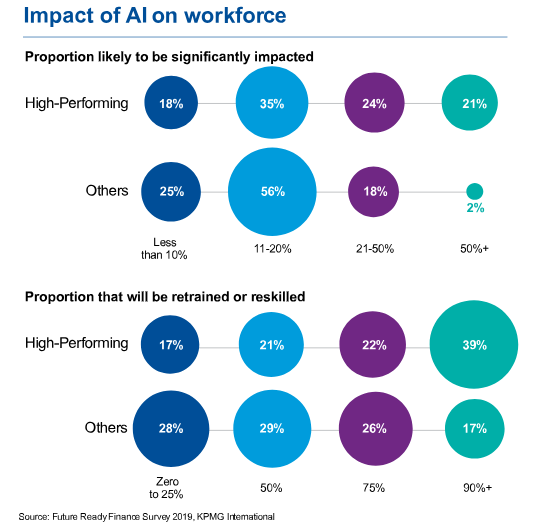
The Role of Education and Reskilling
Addressing the potential challenges posed by AI requires proactive measures to reskill and upskill the workforce. As AI technologies continue to evolve, the demand for workers with expertise in AI development, data science, and related fields is expected to grow. Educational institutions, governments, and employers must collaborate to ensure that workers have access to training programs and resources that equip them with the skills needed to thrive in an AI-driven economy.
Furthermore, fostering a culture of lifelong learning is crucial to preparing individuals for career transitions and new opportunities created by AI. Continuous education and professional development enable workers to adapt to technological advancements and remain competitive in an increasingly digital and interconnected world.
Ethical and Societal Implications
Beyond its economic impact, AI raises important ethical and societal considerations that must be addressed to ensure its responsible deployment and use. Issues such as bias in AI algorithms, data privacy concerns, and the implications of autonomous decision-making systems pose significant challenges that require careful consideration and regulation.
Bias in AI algorithms, for example, can perpetuate existing inequalities and discrimination if not properly addressed during the development and deployment phases. Similarly, the collection and use of personal data by AI systems raise concerns about privacy and security, necessitating robust regulatory frameworks and standards to safeguard individuals’ rights.
While the widespread adoption of AI has the potential to transform industries and improve societal welfare, its impact on employment remains a subject of ongoing debate and scrutiny. AI technologies have the capacity to automate routine tasks, leading to the displacement of certain jobs, but they also create new opportunities and enable workers to focus on tasks that require human skills and expertise.
To maximize the benefits of AI while mitigating its potential challenges, stakeholders must collaborate to develop policies and strategies that prioritize education, reskilling, and the ethical deployment of AI technologies. By investing in human capital and fostering a culture of innovation and lifelong learning, societies can harness the transformative power of AI to create a more inclusive, prosperous, and sustainable future for all.